Technology Advanced Lab
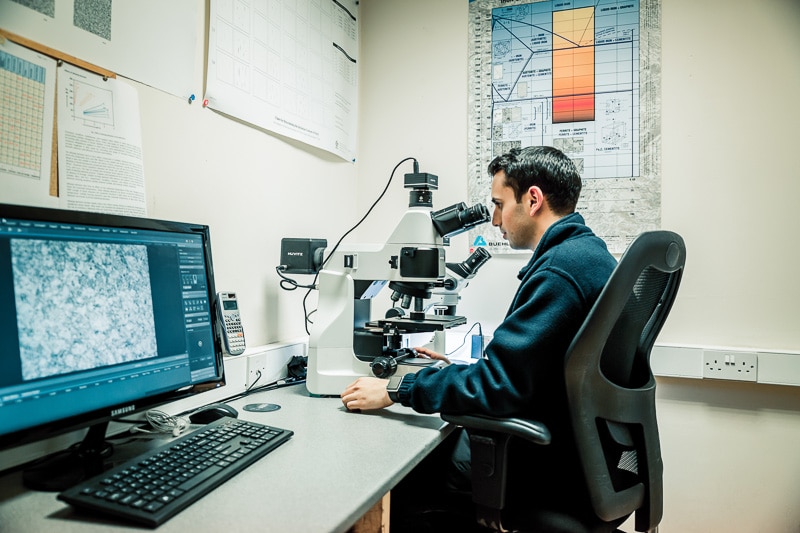
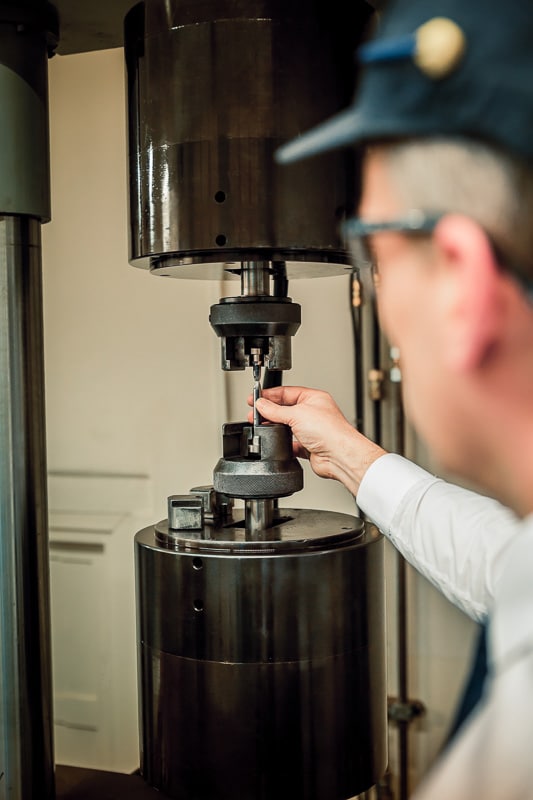
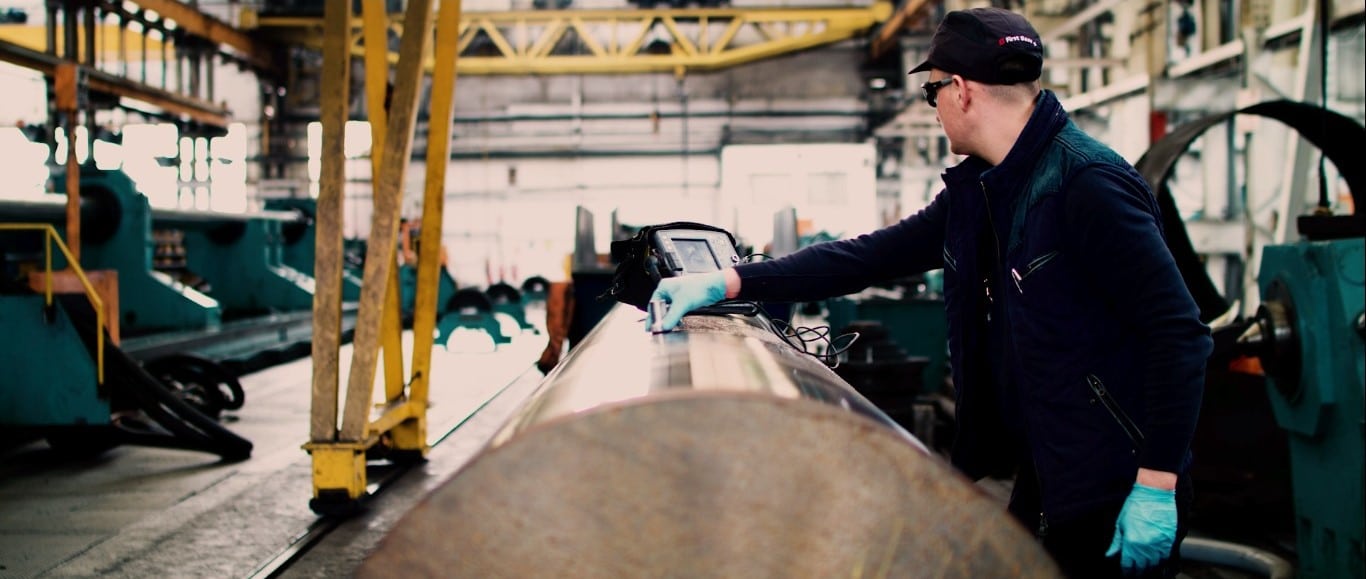
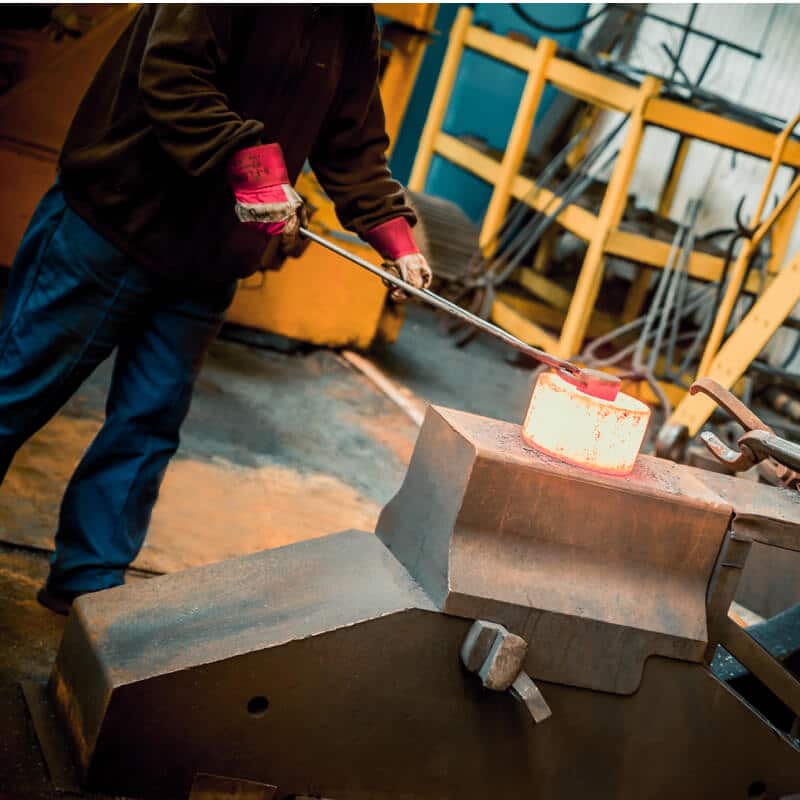
Our technologically advanced lab supports quality control and research and development. Offering non-destructive testing, hardness testing, mechanical testing and metallographic analysis.
We can facilitate a wide range of tests as required by our customer. In addition we test under different climatic conditions from sub-zero to elevated temperatures.